In Islam, pork is considered haram, or forbidden, for several reasons, including scientific ones. One key reason is the potential health risks associated with consuming pork. Pork can carry diseases that can be transmitted to humans, such as trichinosis and tapeworms. Additionally, pork is known to be high in unhealthy fats, which can contribute to heart disease, obesity, and other health problems. Furthermore, pigs are considered unclean animals in Islam, as they often live in dirty environments and consume waste. For these reasons, many Muslims choose to avoid pork in their diets, both for religious and health reasons.
The pig is considered a breeding ground for harmful germs. Scientific evidence supports the view that pork meat is among the least healthy, containing various harmful agents such as cholesterol, fatty acids, bacteria, toxins, and numerous parasites.
Why Pork is Haram: The Scientific Reasons Behind the Islamic Prohibition and why pork is haram scientifically
In Islamic dietary laws, pork is classified as haram, meaning it is forbidden for Muslims to consume. While this prohibition is primarily based on religious beliefs, there are also scientific reasons that support the avoidance of pork in the diet.
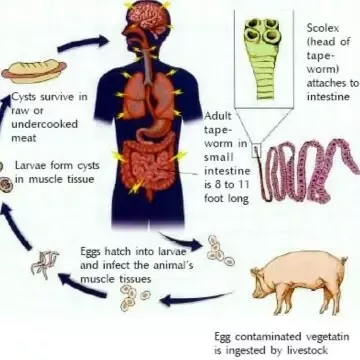
One of the main scientific reasons for avoiding pork is the health risks associated with its consumption. Pork has been linked to various diseases that can be transmitted to humans, including trichinosis, a parasitic infection caused by the roundworm Trichinella spiralis. This parasite can infect humans who consume undercooked or raw pork, leading to symptoms such as muscle pain, fever, and swelling around the eyes. and learn why pork is haram scientifically.
Additionally, pork is known to be high in unhealthy fats, particularly saturated fats. Consuming high amounts of saturated fats has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, obesity, and other health problems. By avoiding pork, individuals can reduce their intake of these harmful fats and lower their risk of developing these conditions.
Another scientific reason for avoiding pork is related to the cleanliness of the animal itself. Pigs are scavengers by nature, often consuming whatever food is available to them, including garbage and waste. This diet can lead to the accumulation of toxins and harmful bacteria in the pig’s body, which can then be passed on to humans through consumption.
In conclusion, while the prohibition of pork in Islam is primarily a religious matter, there are also valid scientific reasons to avoid its consumption. By understanding these reasons, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet and health.
By adhering to the Islamic dietary laws and avoiding pork, individuals can not only fulfill religious obligations but also protect their health. Choosing alternative sources of protein, such as poultry, fish, and legumes, can provide essential nutrients without the associated health risks of pork.
Moreover, the scientific reasons behind the prohibition of pork in Islam highlight the importance of food safety and hygiene. By being mindful of the sources and quality of the food they consume, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting foodborne illnesses and other health issues.
In conclusion, while the prohibition of pork in Islam is rooted in religious teachings, there are clear scientific reasons that support this dietary restriction. By understanding these reasons and making informed choices about their diet, individuals can promote both their physical health and spiritual well-being.

Additionally, avoiding pork can also have positive environmental impacts. Pig farming is often associated with high levels of pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing the demand for pork, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable food system, which is why pork is haram scientifically.
Furthermore, respecting dietary restrictions, including the prohibition of pork, is an important aspect of cultural sensitivity and inclusivity. Understanding and accommodating these restrictions can help foster a more inclusive and respectful society.
In conclusion, the prohibition of pork in Islam is based on both religious teachings and scientific reasoning. By avoiding pork, individuals can protect their health, promote environmental sustainability, and show respect for cultural and religious beliefs.
Embracing a diet that excludes pork can lead to a healthier lifestyle overall. By replacing pork with other nutritious foods, individuals can enjoy a balanced diet that supports their well-being. This dietary choice aligns with the principles of moderation and mindfulness, which are central to Islamic teachings on food consumption.
Moreover, the avoidance of pork encourages individuals to explore a wider variety of foods and cooking methods, fostering creativity in the kitchen. It opens up opportunities to discover new flavors and dishes that are both delicious and nourishing.
In essence, the prohibition of pork in Islam serves as a reminder of the importance of mindful eating and the impact of food choices on health, society, and the environment. By understanding and respecting these teachings, individuals can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Consuming pork can have several disadvantages, including:
- Health Risks: Pork is known to carry various diseases that can be transmitted to humans, such as trichinosis, tapeworms, and salmonella. These infections can lead to serious health issues.
- High Fat Content: Pork is high in unhealthy saturated fats, which can contribute to heart disease, obesity, and other health problems when consumed in excess.
- Cholesterol Levels: Pork is also high in cholesterol, which can raise blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Digestive Issues: Some people may experience digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea, after consuming pork.
- Environmental Impact: Pig farming can have a significant environmental impact, including pollution of waterways and emissions of greenhouse gases.
- Religious and Cultural Beliefs: For those who follow religious or cultural beliefs that prohibit the consumption of pork, consuming pork can go against their values and traditions.
Overall, while pork can be a source of protein and nutrients, it is important to consume it in moderation and be aware of the potential health risks and other disadvantages associated with its consumption.
The medical basis for pork being considered haram, or forbidden, in Islam primarily revolves around the health risks associated with its consumption. Pork has been linked to various diseases and health issues, including:
- Parasitic Infections: Pork can be a host to parasites such as Trichinella spiralis, which causes trichinosis. This parasitic infection can lead to symptoms such as muscle pain, fever, and swelling around the eyes.
- Bacterial Infections: Pork is susceptible to contamination by bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli, which can cause food poisoning and gastrointestinal issues.
- High Fat Content: Pork is high in unhealthy saturated fats, which can contribute to heart disease, obesity, and other health problems when consumed in excess.
- Cholesterol Levels: Pork is also high in cholesterol, which can raise blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Toxins: Pigs are scavenger animals that may consume a variety of substances, including toxins and harmful bacteria. These toxins can accumulate in the pig’s body and be passed on to humans through consumption.
- The prohibition on consuming pork in both Islam and Judaism stems from ancient dietary guidelines focused on food safety. For millennia, both religions have banned the consumption of pork and its derivatives. The Quran explicitly designates certain foods as permissible (halal) and others as forbidden (haram), with pork falling into the latter category.
Due to these health risks, Islamic dietary laws prohibit the consumption of pork. This prohibition serves as a measure to protect individuals from potential health hazards associated with pork consumption.
Additionally, the prohibition of pork in Islam is also based on the concept of cleanliness and purity. Pigs are considered inherently unclean animals in Islamic teachings due to their habits and diet. Pigs are known to be scavengers, often consuming garbage, feces, and other waste. Their digestive systems are less efficient than other animals, leading to the retention of more toxins and potentially harmful substances in their bodies.
Furthermore, pigs do not have sweat glands, which means they are unable to sweat out toxins. This lack of sweating, combined with their diet and living conditions, increases the likelihood of toxins accumulating in their bodies. When consumed by humans, these toxins can pose health risks.
In Islam, cleanliness and purity are highly emphasized, not only in physical cleanliness but also in the cleanliness of one’s actions and thoughts. Therefore, the prohibition of pork can also be seen as a way to promote cleanliness and purity in all aspects of life.

Overall, the medical basis for pork being considered haram in Islam reflects a concern for both physical and spiritual health, emphasizing the importance of moderation, cleanliness, and mindfulness in dietary practices.
Furthermore, the medical basis for the prohibition of pork in Islam aligns with modern scientific understanding of food safety and hygiene. The risks associated with consuming pork, such as parasitic infections and bacterial contamination, are well documented in the scientific literature.
For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes trichinellosis, a disease caused by consuming undercooked pork infected with the parasite Trichinella, as a public health concern. The organization advises the proper cooking and handling of pork to prevent infection.
Similarly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights the risks of bacterial contamination in pork, such as Salmonella and E. coli. These bacteria can cause food poisoning and other gastrointestinal illnesses if pork is not cooked thoroughly or if proper hygiene practices are not followed.
By adhering to the prohibition of pork, Muslims not only follow religious teachings but also potentially reduce their risk of contracting foodborne illnesses and other health issues associated with pork consumption. This dietary restriction serves as a preventive measure to safeguard individuals’ health and well-being.
Moreover, the prohibition of pork in Islam is not unique, as other religions and cultures also have dietary restrictions based on similar principles of cleanliness and health. For example, Judaism also prohibits the consumption of pork, citing similar concerns about health and hygiene.
In essence, the medical basis for pork being considered haram in Islam reflects a holistic approach to health that considers both physical and spiritual well-being. By understanding and respecting these dietary guidelines, individuals can make informed choices that promote their overall health and contribute to a more conscientious society.
Additionally, the prohibition of pork in Islam extends beyond individual health to encompass broader societal and environmental considerations. Pig farming is often associated with environmental issues such as pollution, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions. By avoiding pork, Muslims can contribute to a more sustainable food system and reduce their environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the prohibition of pork in Islam promotes compassion and respect for animals. Pigs are intelligent and sentient beings, and the consumption of pork is seen as a disregard for their welfare. By abstaining from pork, Muslims demonstrate a commitment to treating animals with kindness and compassion.
Overall, the medical basis for pork being considered haram in Islam reflects a comprehensive approach to health and well-being that considers the interconnectedness of individual health, societal values, and environmental sustainability. This dietary restriction serves as a reminder of the importance of mindfulness and moderation in all aspects of life, promoting a balanced and holistic approach to health.
In conclusion, the medical basis for pork being considered haram in Islam is multifaceted. It encompasses health risks such as parasitic and bacterial infections, as well as the high fat and cholesterol content of pork. Additionally, the concept of cleanliness and purity plays a significant role, as pigs are considered unclean animals due to their habits and diet.
By prohibiting the consumption of pork, Islam aims to protect the health and well-being of its followers. This prohibition serves as a reminder of the importance of mindful eating and the impact of dietary choices on health. It also highlights the importance of cleanliness and purity in all aspects of life, promoting a holistic approach to health and well-being.
Furthermore, the medical basis for the prohibition of pork in Islam aligns with modern scientific understanding of food safety and hygiene. The risks associated with consuming pork, such as parasitic infections and bacterial contamination, are well-documented in scientific literature.
For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes trichinellosis, a disease caused by consuming undercooked pork infected with the parasite Trichinella, as a public health concern. The organization advises proper cooking and handling of pork to prevent infection.
Similarly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights the risks of bacterial contamination in pork, such as Salmonella and E. coli. These bacteria can cause food poisoning and other gastrointestinal illnesses if pork is not cooked thoroughly or if proper hygiene practices are not followed.
By adhering to the prohibition of pork, Muslims not only follow religious teachings but also potentially reduce their risk of contracting foodborne illnesses and other health issues associated with pork consumption. This dietary restriction serves as a preventive measure to safeguard individuals’ health and well-being.
Moreover, the prohibition of pork in Islam is not unique, as other religions and cultures also have dietary restrictions based on similar principles of cleanliness and health. For example, Judaism also prohibits the consumption of pork, citing similar concerns about health and hygiene.
In essence, the medical basis for pork being considered haram in Islam reflects a holistic approach to health that considers both physical and spiritual well-being. By understanding and respecting these dietary guidelines, individuals can make informed choices that promote their overall health and contribute to a more conscientious society.
Additionally, the prohibition of pork in Islam extends beyond individual health to encompass broader societal and environmental considerations. Pig farming is often associated with environmental issues such as pollution, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions. By avoiding pork, Muslims can contribute to a more sustainable food system and reduce their environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the prohibition of pork in Islam promotes compassion and respect for animals. Pigs are intelligent and sentient beings, and the consumption of pork is seen as a disregard for their welfare. By abstaining from pork, Muslims demonstrate a commitment to treating animals with kindness and compassion.

Leave a Reply