Malunion of a Fractured Bone:its causes, warning signs, complications, and effective treatment options to restore mobility and bone health.
This document provides a comprehensive overview of malunion, a complication of bone fractures where the bone heals in an abnormal position. It discusses the causes, diagnosis, potential problems, and various treatment options available to correct malunion and restore proper function.

Understanding Malunion
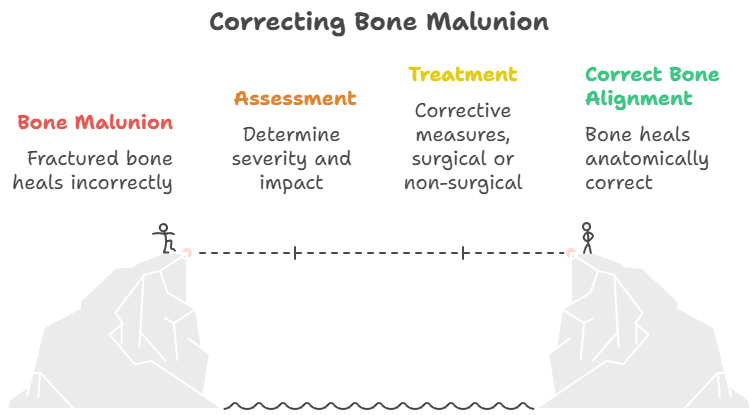
Malunion occurs when a fractured bone heals in a position that is not anatomically correct. This can result in a variety of problems, ranging from cosmetic deformities to significant functional limitations. The severity of the malunion and its impact on the individual depend on several factors, including the bone involved, the degree of displacement or angulation, and the patient’s activity level.
Causes of Malunion
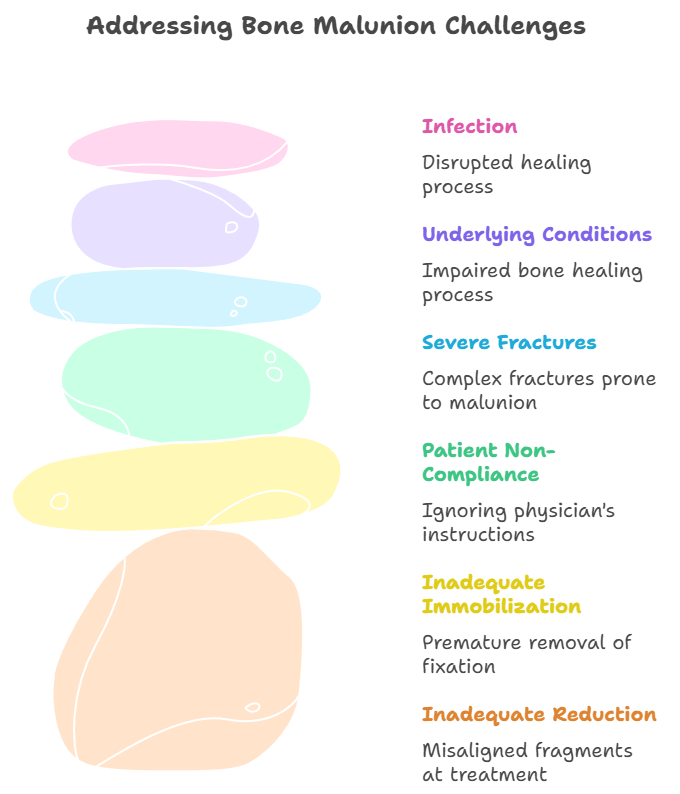
Several factors can contribute to the development of malunion:
- Inadequate Reduction: Failure to properly align the fractured bone fragments during the initial treatment is a primary cause.
- Inadequate Immobilization: Insufficient or premature removal of casts, splints, or other fixation devices can allow the bone fragments to shift during the healing process.
- Patient Non-Compliance: Failure to follow the physician’s instructions regarding weight-bearing restrictions, activity limitations, or brace usage can compromise fracture healing.
- Severe Fractures: Complex fractures, such as those involving multiple fragments or significant bone loss, are more prone to malunion.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as osteoporosis or metabolic bone diseases, can impair bone healing and increase the risk of malunion.
- Infection: Infection at the fracture site can disrupt the healing process and lead to malunion.
Diagnosis of Malunion
Diagnosing malunion typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging studies:
- Physical Examination: The physician will assess the alignment of the bone, range of motion, stability, and any associated pain or tenderness. They will also look for any visible deformities or limb length discrepancies.
- X-rays: X-rays are the primary imaging modality used to evaluate the alignment of the healed fracture. They can reveal the degree of displacement, angulation, or rotation.
- CT Scans: CT scans provide more detailed images of the bone and can be helpful in assessing complex malunions or those involving joints.
- MRI Scans: MRI scans can be used to evaluate soft tissue structures around the fracture site, such as ligaments, tendons, and muscles. They can also help identify any associated injuries or complications.
Problems Caused by Malunion
Malunion can lead to a variety of problems, depending on the location and severity of the deformity:
- Pain: Malalignment can cause chronic pain due to abnormal stress on joints, muscles, and ligaments.
- Limited Range of Motion: Malunion can restrict joint movement and impair function.
- Deformity: Visible deformities can be cosmetically unappealing and may affect self-esteem.
- Limb Length Discrepancy: Malunion can result in a shorter or longer limb, leading to gait abnormalities and back pain.
- Arthritis: Long-term malalignment can accelerate the development of arthritis in the affected joint.
- Nerve Compression: In some cases, malunion can compress nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness.
- Nonunion: In rare cases, malunion can lead to nonunion, where the fracture fails to heal completely.
Treatment Options for Malunion
The treatment for malunion depends on the severity of the deformity, the patient’s symptoms, and their overall health. Treatment options range from conservative measures to surgical correction.
Non-Surgical Treatment
- Observation: Mild malunions that do not cause significant symptoms may be managed with observation and pain medication.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve range of motion, strength, and function.
- Orthotics: Braces or orthotics can provide support and stability to the affected limb.
- Pain Management: Pain medications, such as NSAIDs or opioids, can help relieve pain.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical correction of malunion is typically considered when non-surgical treatments fail to provide adequate relief or when the deformity is severe enough to cause significant functional limitations. The goals of surgery are to restore proper alignment of the bone, improve joint function, and relieve pain.
- Osteotomy: Osteotomy involves cutting the bone at or near the site of the malunion and realigning it into the correct position. The bone fragments are then fixed with plates, screws, or other fixation devices.
- Bone Grafting: Bone grafting may be necessary to fill any gaps created during the osteotomy or to promote bone healing.
- Joint Replacement: In cases where malunion has led to severe arthritis, joint replacement may be an option.
- Limb Lengthening/Shortening: If malunion has resulted in a significant limb length discrepancy, limb lengthening or shortening procedures may be considered.
- Ilizarov Technique: The Ilizarov technique involves using a circular external fixator to gradually correct the deformity over time. This technique is often used for complex malunions or those involving significant bone loss.
Considerations for Surgical Correction
Surgical correction of malunion is a complex procedure that requires careful planning and execution. Factors to consider include:
- Timing of Surgery: The timing of surgery depends on the age of the malunion and the patient’s overall health. In general, it is best to wait until the bone has fully healed before attempting surgical correction.
- Type of Osteotomy: The type of osteotomy performed depends on the location and severity of the malunion.
- Fixation Method: The choice of fixation method depends on the type of osteotomy and the stability of the bone.
- Potential Complications: Potential complications of surgery include infection, nonunion, nerve damage, and blood clots.
Rehabilitation After Surgery
Rehabilitation after surgery is essential for restoring function and preventing complications. The rehabilitation program typically includes:
- Pain Management: Pain medications are used to control pain after surgery.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is used to improve range of motion, strength, and function.
- Weight-Bearing Restrictions: Weight-bearing restrictions are typically imposed for several weeks after surgery to allow the bone to heal properly.
Conclusion
Malunion is a complication of bone fractures that can lead to a variety of problems. Treatment options range from conservative measures to surgical correction. The best treatment approach depends on the severity of the deformity, the patient’s symptoms, and their overall health. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for restoring function and preventing long-term complications.
Disclaimer:Dr. Mohammed Abdul Azeem Siddiqui, MBBS
Registered Medical Practitioner (Reg. No. 39739)
With over 30 years of dedicated clinical experience, Dr. Siddiqui has built his career around one clear mission: making quality healthcare affordable, preventive, and accessible.
He is deeply passionate about:
- Early disease diagnosis – empowering patients with timely detection and reducing complications.
- Preventive healthcare – guiding individuals and families towards healthier, longer lives through lifestyle interventions and screenings.
- Affordable treatments – ensuring cost-effective, evidence-based medical solutions that reach people from all walks of life.
Through his blog, Dr. Siddiqui shares practical health insights, early warning signs, and preventive strategies that readers can trust. Every article is rooted in evidence-based medicine and enriched by decades of hands-on clinical practice.
Contact us on: powerofprevention@outlook.com
📌 Disclaimer: The content in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not replace personalized medical consultation. For specific health concerns, please consult your physician.
**********This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through them, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thanks for supporting the blog!***************************************************************
Leave a Reply